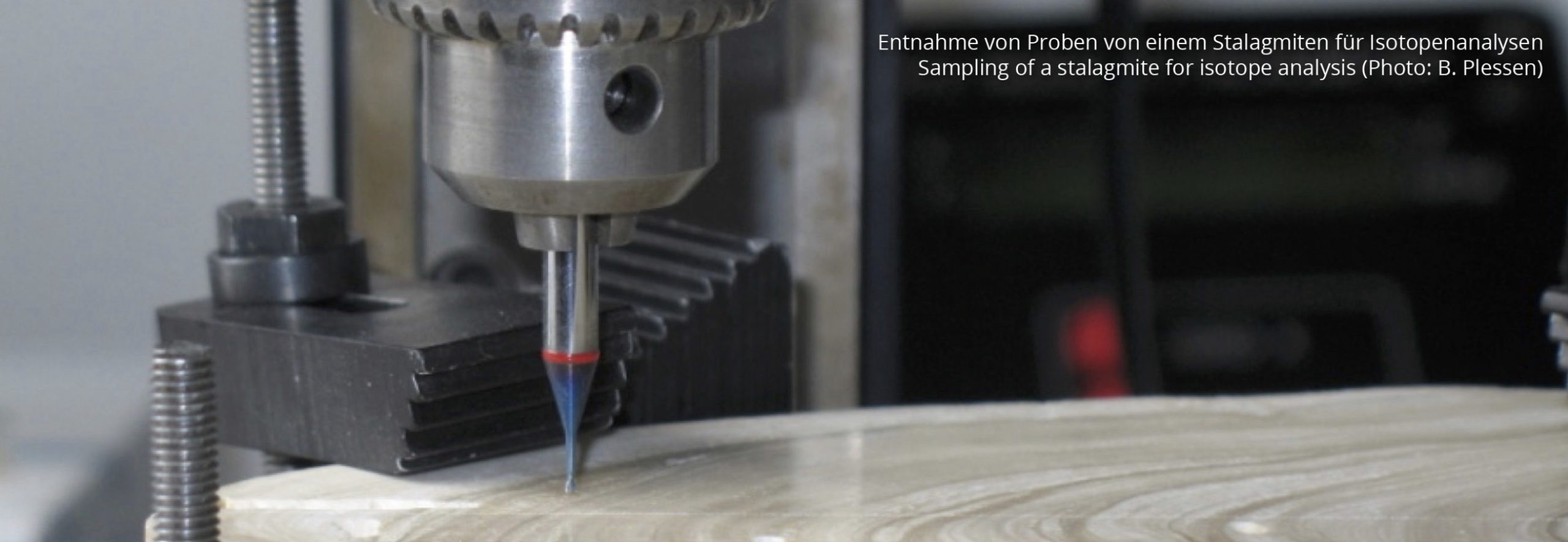
Probe
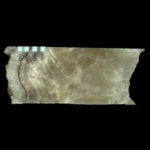
BB-15
art der probe
Sinter
lage
Osthöhle, flächiger Wandsinter aus großer Kernbohrung neben „Hochzeitstorte“
probennahme
April … November 2008?: TLUG/ TLUBN?
verbleib
LIAG Hannover
LIAG-Bezeichnung: ID10356
nur ein Viertel des Kerns beim LIAG, Rest bei TLUG?
Scheibe gesägt aus der Probe beim LIAG und 2021 an die JGU geschickt
datierungDatierung Um einem Stalagmiten oder gar einer einzelnen Wachstumslage im Stalagmiten ein Alter zuordnen zu können, muß eine Datierung durchgeführt werden. Dies erfolgt in der Regel radiometrisch, d. h. über die Messung von Zerfallsprodukten (siehe auch U/Th-Datierung).
TIMS 1272-1383: 55,4 bis 8,7 ka BPka BP Mit "ka BP" sind "Tausend Jahre vor 1950" gemeint. Das "BP" steht für "before present", was in der Paläoklima-Wissenschaft als 1950 festgelegt wurde. "11.000 ka BP" bedeuted also 11 Tausend Jahre vor 1950, oder unter Verwendung unseres gewohnten Kalenders: 9050 v. Chr.
U/ThU/Th-Datierung Die U/Th-Datierung ist eine sehr präzise radiometrische Altersbestimmung auf Basis der Uran-Thorium-Zerfallsreihe. Das Uran zerfällt mit bekannten Halbwertszeiten (245.500 Jahre) zum Tochterelement Thorium. Stalagmiten bauen bei ihrem Wachstum (fast) nur das wasserlösliche Uran ein, während das schlecht bewegliche Thorium zum größten Teil im Boden und Epikarst über der Höhle verbleibt. Das kann man nutzen, um die Zeit zu berechnen, die seit der Ausfällung der untersuchten Karbonatprobe vergangen ist. Moderne massenspektrometrische Verfahren erlauben Altersbestimmungen mit der U/Th-Methode bis zu 700.000 Jahren vor Heute., Lösungsalter 8, Laser ablation 163, gemessen an der JGU Mainz
alter
6.85 ± 0.01 ka BP (top)
58.6 ± 0.09 ka BP (bottom)
proxiesProxy Umwelt- und Klimainformationen aus der Vergangenheit sind nicht direkt verfügbar, weil niemand da war, der diese messen und aufzeichnen konnte. Daher ist man darauf angewiesen, diese Informationen indirekt aus anderen Informationen abzuleiten, wie z. B. Baumringe, das Verhältnis von Sauerstoffisotopen, Spurenelementen, Mächtigkeit von Sedimentschichten usw. Diese Art von Daten nennt man Proxies, was aus dem englischen stammt und „Stellvertreter“ bedeutet.
stabile IsotopenIsotop Chemische Elemente können aus verschieden aufgebauten Atomen gebildet sein. Die Anzahl Protonen im Atomkern ist zwar dabei gleich, aber die Anzahl der Neutronen kann variieren. Man spricht dann von Isotopen, deren Massen kleine, aber messbare Unterschiede aufweisen. Der Atomkern des Sauerstoffs besteht z. B. aus 8 Protonen und in der Regel aus 8 Neutronen. Es gibt aber auch Sauerstoff, dessen Kerne aus 8 Protonen und 9 oder 10 Neutronen bestehen (neben selteneren, instabilen Sauerstoffisotopen). Um das zu kennzeichnen, gibt man zusätzlich zum chemischen Symbol noch die Massenzahl (Summe aus Protonen und Neutronen) an, also 16O, 17O oder 18O. Die unterschiedlichen Isotope verhalten sich zwar chemisch identisch, physikalisch aber - aufgrund ihres unterschiedlichen Gewichtes - leicht unterschiedlich. Damit stellen sie äusserst wertvolle Marker dar, die uns wichtige Hinweise zur Änderung des Klimas, der Umgebungsvegetation, Bodenaktivität und vielem mehr geben. δ13C and δ18O (264 samples)
Gemessen am LIAG
stabile Isotopen δ13C and δ18O (542 samples, nur MIS3)
Gemessen am MPIC, Mainz
LOP (19 Messungen)
Gemessen durch J. Homann an der JGU, Mainz (Chemie)
publikationen
Klose, J.; Breitenbach, S.; Weber, M.; Vonhof, H.; Schr{"o}der, B.; Marwan, N.; Katzschmann, L.; Scholz, D.
Vortrag, Climate Change – The Karst Record X (KR10) Conference, University of Cape Town (South Africa), 27.03.2025.
@misc{klose2025_03,
title = {Precisely dated flowstone growth phases as a proxy for particularly warm climate conditions during MIS 3 in Central Europe},
author = {J. Klose and S. Breitenbach and M. Weber and H. Vonhof and B. Schr{"o}der and N. Marwan and L. Katzschmann and D. Scholz},
url = {https://web.archive.org/web/20250619175132/https://uctcmc.eventsair.com/the-10th-international-climate-change-the-karst-record-kr10-conference/
https://bbh.pik-potsdam.de/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/KR10-abstract_J.Klose_.pdf},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-03-27},
urldate = {2025-03-27},
address = {Climate Change – The Karst Record X (KR10) Conference, University of Cape Town (South Africa)},
abstract = {The last glacial period and especially Marine Isotope Stage 3 (MIS 3, ca. 60–30 ka) was characterised by rapid climate oscillations and periodic warm phases. While first discovered in Greenland ice cores, these warm Greenland Interstadials (GIs) have been identified in numerous climate records globally with a strong emphasis on the northern hemisphere and especially the North Atlantic region. However, only few speleothem records from Central Europe are available, presumably due to too cold and dry climate conditions leading to unfavourable conditions for speleothem growth. Here, we present a composite record of flowstones from Bleßberg Cave, Germany, showing episodic speleothem deposition during the last glacial period contemporaneous with individual GIs and revealing Central European warm phases during MIS 3.
By combining high-resolution solution-based and in-situ laser ablation ^{230}Th/U-dating, we accurately determined the timing and duration of eight particularly warm periods during MIS 3. These favourable climatic conditions for speleothem growth occurred intermittently from around 60 to 32 ka, lasting much longer than previously reported in other speleothem records from Central Europe. The onset of speleothem growth lagged behind that of the GIs, covering approximately 88% of their total duration during the early phase and around 25% during the middle and late phases of MIS 3. These findings indicate a trend of progressive climatic cooling during MIS 3, with the phases of speleothem growth representing persistent warm phases in Central Europe.
In addition, the Bleßberg flowstones are highly sensitive to climate change and particularly short-term temperature fluctuations. The longest continuous growth phase of the Bleßberg speleothems coincides with GI 14, the longest GI of MIS 3. We applied a multi-proxy approach (i.e., stable isotopes, trace elements, LOPs, Ca isotopes, fluid inclusions and fluid inclusion-based temperature reconstructions), which revealed two centennial-scale cold events during GI 14. One of them coincides with cold event GI 14b in the Greenland ice core record, which has not been discussed in any other terrestrial climate record from Central Europe yet. Our results document Central European warm phases during MIS 3, indicate rapid regional temperature fluctuations and the absence of continuous permafrost in this region.},
howpublished = {Vortrag},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {presentation}
}
By combining high-resolution solution-based and in-situ laser ablation 230Th/UU/Th-Datierung Die U/Th-Datierung ist eine sehr präzise radiometrische Altersbestimmung auf Basis der Uran-Thorium-Zerfallsreihe. Das Uran zerfällt mit bekannten Halbwertszeiten (245.500 Jahre) zum Tochterelement Thorium. Stalagmiten bauen bei ihrem Wachstum (fast) nur das wasserlösliche Uran ein, während das schlecht bewegliche Thorium zum größten Teil im Boden und Epikarst über der Höhle verbleibt. Das kann man nutzen, um die Zeit zu berechnen, die seit der Ausfällung der untersuchten Karbonatprobe vergangen ist. Moderne massenspektrometrische Verfahren erlauben Altersbestimmungen mit der U/Th-Methode bis zu 700.000 Jahren vor Heute.-dating, we accurately determined the timing and duration of eight particularly warm periods during MIS 3. These favourable climatic conditions for speleothem growth occurred intermittently from around 60 to 32 ka, lasting much longer than previously reported in other speleothem records from Central Europe. The onset of speleothem growth lagged behind that of the GIs, covering approximately 88% of their total duration during the early phase and around 25% during the middle and late phases of MIS 3. These findings indicate a trend of progressive climatic cooling during MIS 3, with the phases of speleothem growth representing persistent warm phases in Central Europe.
In addition, the Bleßberg flowstones are highly sensitive to climate change and particularly short-term temperature fluctuations. The longest continuous growth phase of the Bleßberg speleothems coincides with GI 14, the longest GI of MIS 3. We applied a multi-proxyProxy Umwelt- und Klimainformationen aus der Vergangenheit sind nicht direkt verfügbar, weil niemand da war, der diese messen und aufzeichnen konnte. Daher ist man darauf angewiesen, diese Informationen indirekt aus anderen Informationen abzuleiten, wie z. B. Baumringe, das Verhältnis von Sauerstoffisotopen, Spurenelementen, Mächtigkeit von Sedimentschichten usw. Diese Art von Daten nennt man Proxies, was aus dem englischen stammt und „Stellvertreter“ bedeutet. approach (i.e., stable isotopes, trace elements, LOPs, Ca isotopes, fluid inclusions and fluid inclusion-based temperature reconstructions), which revealed two centennial-scale cold events during GI 14. One of them coincides with cold event GI 14b in the Greenland ice core record, which has not been discussed in any other terrestrial climate record from Central Europe yet. Our results document Central European warm phases during MIS 3, indicate rapid regional temperature fluctuations and the absence of continuous permafrostPermafrost Unter Permafrost versteht man dauerhaft gefrorenen Boden, der auch im Sommer nicht auftaut. In Mitteleuropa gab es während den Eiszeiten Permafrost. in this region.
Klose, Jennifer; Weber, Michael; Scholz, Denis
Central European warm phases recorded by episodic speleothem growth during MIS 3 Artikel
In: communications earth & environment, Bd. 5, S. 719, 2024.
@article{klose2024,
title = {Central European warm phases recorded by episodic speleothem growth during MIS 3},
author = {Jennifer Klose and Michael Weber and Denis Scholz},
doi = {10.6084/m9.figshare.27223863.v1},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-11-20},
urldate = {2024-11-20},
journal = {communications earth & environment},
volume = {5},
pages = {719},
abstract = {Speleothems provide exceptional age control and are a valuable archive for the identification of warm phases in temperate climates. Here we present a speleothem composite record from Germany, which shows episodic growth during the last glacial period, coinciding with several Greenland Interstadials. Using a combined approach of high-resolution solution and in-situ laser ablation 230Th/U-dating, we were able to precisely constrain the timing and duration of several particularly warm phases during Marine Isotope Stage 3. Climatic conditions favourable for speleothem growth occurred episodically until 32,000 years ago, much longer than reported from existing speleothem records. The inception of speleothem growth lags the onset of Greenland Interstadials and covers approximately 88% of their total duration during early, and approximately 25% during middle and late Marine Isotope Stage 3. This indicates progressive climatic cooling during Marine Isotope Stage 3, with the speleothem growth phases representing persistent Central European warm phases.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Klose, Jennifer
Quantitative multi-proxy climate reconstruction for MIS 3 in Central Europe based on precisely dated speleothems from Bleßberg Cave, Germany Promotionsarbeit
2024.
@phdthesis{klose2023phd,
title = {Quantitative multi-proxy climate reconstruction for MIS 3 in Central Europe based on precisely dated speleothems from Bleßberg Cave, Germany},
author = {Jennifer Klose},
editor = {Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz},
url = {https://bbh.pik-potsdam.de/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Klose_Thesis_Jennifer-Klose.pdf},
doi = {10.25358/openscience-10558},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-05-01},
urldate = {2024-05-01},
abstract = {Speläotheme zeichnen sich als sensitive Klimaarchive aus und haben sich in letzten
Jahrzehnten als solche etabliert. Sie haben das Potential wertvolle Informationen über das
Paläoklima kontinuierlich aufzuzeichnen und können mit den Uran-
Ungleichgewichtsmethoden präzise datiert werden. Das Berechnen von unabhängigen
Altersmodellen kombiniert mit Analysen verschiedener Klimaproxys, wie δ18O und δ13C,
Spurenelementen oder Tropfwassereinschlüssen ermöglicht es, hochaufgelöste
Paläoklimarekonstruktionen zu erstellen.
Dansgaard-Oeschger (DO)-Ereignisse sind kurzfristige Klimaschwankungen über
einige hunderte oder wenige tausende Jahre, welche vor allem während der marinen
Isotopenstufe 3 (MIS 3, ca. 60 - 30 ka BP) auftraten. Obwohl erste Beweise für die
Ereignisse in grönländischen Eisbohrkernen entdeckt wurden, sind sie mittlerweile global
nachweisbar. DO-Ereignisse zeichnen sich durch eine rasche Erwärmung, gefolgt von
gradueller Abkühlung aus, während das MIS 3 generell als eine kältere Periode definiert
ist. Daher wurde die Tatsache, dass bisher kaum zentraleuropäische Speläotheme aus dem
MIS 3 gefunden wurden, mit zu kaltem oder trockenem Klima begründet. Im Rahmen
dieser Arbeit wurden drei MIS 3 Speläotheme aus der Bleßberg Höhle in Deutschland
detailliert untersucht. Durch die Kombination von lösungs-basierter und in-situ
Laserablation 230Th/U-Datierung konnte das komplexe Wachstum der Proben präzise
aufgeschlüsselt werden.
Es konnten mehrere Wachstumsepisoden im MIS 3 identifiziert werden, welche primär
zeitgleich zu DO-Ereignissen in Grönland auftraten. Die Wachstumsphasen wurde daher
als eigenständiger Proxy für günstige Klimabedingungen für Speläothemwachstum
etabliert, d.h. Perioden mit ausreichender Boden- und Vegetationsbedeckung über der
Höhle und der Möglichkeit das Tropfwasser in die Höhle gelangt. Darüber hinaus wurde
eine multi-Proxy Analyse durchgeführt mit dem Ziel möglichst vielfältige Informationen
über das MIS 3 in Mitteleuropa zu erhalten. Ein langfristiger Trend zeigt die generelle
Verschlechterung des Klimas mit Fortschreiten des MIS 3 auf. Eine besonders warme und
kontinuierliche Wachstumsphase trat zeitgleich mit DO14 auf. Außerdem wurden zwei
kurzzeitige Kälteereignisse innerhalb des DO14 aufgezeichnet, welches die hohe
Sensitivität der Speläotheme aus der Bleßberg Höhle verdeutlicht.
Weitere kurzzeitige Klimaereignisse wurden während des spätglazialen Teils der
Speläothem-Proben (ca. 14,5 - 1,7 ka BP) aufgezeichnet und ein hochauflösender multi-
Proxy-Datensatz, der das Holozän (11,7 ka BP - rezent) bis 0,6 ka BP abdeckt, wurde
erstellt.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}
Jahrzehnten als solche etabliert. Sie haben das Potential wertvolle Informationen über das
Paläoklima kontinuierlich aufzuzeichnen und können mit den Uran-
Ungleichgewichtsmethoden präzise datiert werden. Das Berechnen von unabhängigen
AltersmodellenAltersmodell Nach der Datierung eines Stalagmiten werden allen anderen Messungen (z. B. Isotopenverhältnisse), die ursprünglich entlang einer Längen-Achse durchgeführt wurden, ein Alter zugeordnet. kombiniert mit Analysen verschiedener Klimaproxys, wie δ18O und δ13C,
Spurenelementen oder Tropfwassereinschlüssen ermöglicht es, hochaufgelöste
Paläoklimarekonstruktionen zu erstellen.
Dansgaard-Oeschger (DO)-Ereignisse sind kurzfristige Klimaschwankungen über
einige hunderte oder wenige tausende Jahre, welche vor allem während der marinen
Isotopenstufe 3 (MIS 3, ca. 60 - 30 ka BP) auftraten. Obwohl erste Beweise für die
Ereignisse in grönländischen Eisbohrkernen entdeckt wurden, sind sie mittlerweile global
nachweisbar. DO-Ereignisse zeichnen sich durch eine rasche Erwärmung, gefolgt von
gradueller Abkühlung aus, während das MIS 3 generell als eine kältere Periode definiert
ist. Daher wurde die Tatsache, dass bisher kaum zentraleuropäische Speläotheme aus dem
MIS 3 gefunden wurden, mit zu kaltem oder trockenem Klima begründet. Im Rahmen
dieser Arbeit wurden drei MIS 3 Speläotheme aus der Bleßberg Höhle in Deutschland
detailliert untersucht. Durch die Kombination von lösungs-basierter und in-situ
Laserablation 230Th/U-Datierung konnte das komplexe Wachstum der Proben präzise
aufgeschlüsselt werden.
Es konnten mehrere Wachstumsepisoden im MIS 3 identifiziert werden, welche primär
zeitgleich zu DO-Ereignissen in Grönland auftraten. Die Wachstumsphasen wurde daher
als eigenständiger ProxyProxy Umwelt- und Klimainformationen aus der Vergangenheit sind nicht direkt verfügbar, weil niemand da war, der diese messen und aufzeichnen konnte. Daher ist man darauf angewiesen, diese Informationen indirekt aus anderen Informationen abzuleiten, wie z. B. Baumringe, das Verhältnis von Sauerstoffisotopen, Spurenelementen, Mächtigkeit von Sedimentschichten usw. Diese Art von Daten nennt man Proxies, was aus dem englischen stammt und „Stellvertreter“ bedeutet. für günstige Klimabedingungen für Speläothemwachstum
etabliert, d.h. Perioden mit ausreichender Boden- und Vegetationsbedeckung über der
Höhle und der Möglichkeit das Tropfwasser in die Höhle gelangt. Darüber hinaus wurde
eine multi-Proxy Analyse durchgeführt mit dem Ziel möglichst vielfältige Informationen
über das MIS 3 in Mitteleuropa zu erhalten. Ein langfristiger Trend zeigt die generelle
Verschlechterung des Klimas mit Fortschreiten des MIS 3 auf. Eine besonders warme und
kontinuierliche Wachstumsphase trat zeitgleich mit DO14 auf. Außerdem wurden zwei
kurzzeitige Kälteereignisse innerhalb des DO14 aufgezeichnet, welches die hohe
Sensitivität der Speläotheme aus der Bleßberg Höhle verdeutlicht.
Weitere kurzzeitige Klimaereignisse wurden während des spätglazialen Teils der
SpeläothemSpeläothem Sekundäre Mineralablagerungen in Höhlen, wie Sinter, Stalagmiten, Stalaktiten, usw.-Proben (ca. 14,5 - 1,7 ka BP) aufgezeichnet und ein hochauflösender multi-
Proxy-Datensatz, der das HolozänHolozän Der jüngste Abschnitt der geologischen Zeitgeschichte, etwa die letzten 11.700 Jahre. (11,7 ka BP - rezent) bis 0,6 ka BP abdeckt, wurde
erstellt.
Klose, J.; Scholz, D.; Weber, M.; Vonhof, H.; Plessen, B.; Breitenbach, S.; Marwan, N.
Timing of Dansgaard-Oeschger events in Central Europe based on three precisely dated speleothems from Bleßberg Cave, Germany Konferenzberichte
Poster, 2023, (Summer School on Speleothem Sciences 2023, Sao Paulo).
@proceedings{klose2023poster,
title = {Timing of Dansgaard-Oeschger events in Central Europe based on three precisely dated speleothems from Bleßberg Cave, Germany},
author = {J. Klose and D. Scholz and M. Weber and H. Vonhof and B. Plessen and S. Breitenbach and N. Marwan},
editor = {Summer School on Speleothem Sciences 2023, Sao Paulo},
url = {https://bbh.pik-potsdam.de/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/klose_SummerschoolSaoPaulo2023.pdf},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-08-07},
urldate = {2023-08-07},
abstract = {The last glacial period and especially Marine Isotope stage 3 (MIS 3, ca. 57 - 27 ka) was characterized by various climate oscillations (i.e., rapid increases in temperature, followed by a gradual cooling, the Dansgaard-Oeschger (D/O) events), which were first discovered in Greenland ice cores. Although their causes are still not fully understood, clear evidence for their supra-regional character was found in various climate records around the globe. However, European speleothem samples, which grew during MIS 3, are limited and mainly restricted to alpine regions, where glacier meltwater enabled speleothem growth, and to south/south-western parts of Europe characterised by a generally warmer climate. This led to the opinion that it was too cold and/or too dry in central Europe for speleothem growth. Here we present three speleothem (flowstone) records from Bleßberg Cave, Germany, which grew during MIS 3.
All flowstones show episodical growth patterns with distinctive, thin growth phases. Potential contamination deriving form detrital material deposited during hiatuses between individual growth phases, open-system behaviour around the hiatuses and the limited thickness of the growth layers are the biggest challenges during sampling for 230Th/U dating. By combination of different sampling techniques (i.e., laser ablation and micro-milling) in addition to the common approach of handheld drilling and due to the relatively high 238U concentration of the samples (approx. 0.4 – 1 µg/g), we were able to date even the thinnest growth layers (< 2 mm) of the Bleßberg flowstones with a very high precision (i.e., with 2σ-age uncertainties of a few hundred years or even lower).
The timing of the growth phases of the Bleßberg flowstones correlates with several D/O events recorded in the Greenland ice cores. This proves that at least some phases of MIS 3 had favourable climate conditions for speleothem growth in Central Europe. In addition, the analysis of the stable oxygen and carbon isotopes (δ18O and δ13C) for all three flowstones revealed several D/O events, which have not been recorded in any other speleothem from central Europe so far. This will enhance our understanding of climate variability during MIS 3 and specific D/O events in central Europe.},
howpublished = {Poster},
note = {Summer School on Speleothem Sciences 2023, Sao Paulo},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
All flowstones show episodical growth patterns with distinctive, thin growth phases. Potential contamination deriving form detrital material deposited during hiatuses between individual growth phases, open-system behaviour around the hiatuses and the limited thickness of the growth layers are the biggest challenges during sampling for 230Th/U dating. By combination of different sampling techniques (i.e., laser ablation and micro-milling) in addition to the common approach of handheld drilling and due to the relatively high 238U concentration of the samples (approx. 0.4 – 1 µg/g), we were able to date even the thinnest growth layers (< 2 mm) of the Bleßberg flowstones with a very high precision (i.e., with 2σ-age uncertainties of a few hundred years or even lower).
The timing of the growth phases of the Bleßberg flowstones correlates with several D/O events recorded in the Greenland ice cores. This proves that at least some phases of MIS 3 had favourable climate conditions for speleothem growth in Central Europe. In addition, the analysis of the stable oxygen and carbon isotopes (δ18O and δ13C) for all three flowstones revealed several D/O events, which have not been recorded in any other speleothem from central Europe so far. This will enhance our understanding of climate variability during MIS 3 and specific D/O events in central Europe.
Klose, J.; Scholz, D.; Weber, M.; Vonhof, H.; Plessen, B.; Breitenbach, S.; Marwan, N.
Timing and progression of Dansgaard-Oeschger events in Central Europe based on three precisely dated speleothems from Bleßberg Cave, Germany Konferenzberichte
Poster, 2023, (XXI INQUA Conference, Rome (Italy)).
@proceedings{klose2023,
title = {Timing and progression of Dansgaard-Oeschger events in Central Europe based on three precisely dated speleothems from Bleßberg Cave, Germany},
author = {J. Klose and D. Scholz and M. Weber and H. Vonhof and B. Plessen and S. Breitenbach and N. Marwan},
editor = {XXI INQUA Conference, Rome (Italy)},
year = {2023},
date = {2023-07-19},
urldate = {2023-07-19},
abstract = {Speleothems can be dated with unprecedented precision using U-series disequilibrium methods and provide numerous climate proxies, such as stable oxygen (δ18O) and carbon isotopes (δ13C) or trace elements, resulting in long, sometimes continuous climate proxy records. Therefore, speleothems have great potential for reconstruction of past climate variability during Marine Isotope Stage (MIS) 3 and precise determination of the timing and duration of Dansgaard-Oeschger (D/O) events. While first discovered in Greenland ice cores, various speleothem records around the globe provided clear evidence for the supra-regional character of the D/O events. However, MIS 3 speleothem records from Central Europe are very limited. Here we present three spleothem (flowstone) MIS 3 records from Bleßberg Cave, Germany.
All flowstones show episodic growth with distinctive, partially very thin (<2 mm) growth phases, interrupted by visible hiatuses consisting of detrital material. Precise and accurate 230Th/U dating of the individual growth phases is challenging due to potential detrital contamination from these layers. Combining different sampling and analytical techniques, we were able to date even the thinnest growth layers with very high precision, i.e., 2σ-age uncertainties of at most a few hundred years.
The timing of the growth phases aligns with several D/O events, which have not been recorded in other Central European speleothems yet. The δ18O and δ13C records of all three flowstones are highly correlated which suggests a dominant process influencing both isotope systems. Comparison with the Sr and Mg records provides evidence for a strong influence of Prior Calcite Precipitation (PCP) in the aquifer above and inside the cave on the stable isotope and trace element signals. In addition, all proxy records are interpreted as evidence for past changes in precipitation and vegetation density and document a clear trend from more humid climate during early MIS 3 (ca. 57 – 50 ka) to less humid conditions during mid and late MIS 3 (ca. 45 – 30 ka).
Our multi-proxy approach thus allows us not only to precisely determine the timing, duration, and progression of several D/O events, but also to deepen our general understanding of climate variability during MIS 3 in Central Europe.},
howpublished = {Poster},
note = {XXI INQUA Conference, Rome (Italy)},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
All flowstones show episodic growth with distinctive, partially very thin (<2 mm) growth phases, interrupted by visible hiatuses consisting of detrital material. Precise and accurate 230Th/U dating of the individual growth phases is challenging due to potential detrital contamination from these layers. Combining different sampling and analytical techniques, we were able to date even the thinnest growth layers with very high precision, i.e., 2σ-age uncertainties of at most a few hundred years.
The timing of the growth phases aligns with several D/O events, which have not been recorded in other Central European speleothems yet. The δ18O and δ13C records of all three flowstones are highly correlated which suggests a dominant process influencing both isotope systems. Comparison with the Sr and Mg records provides evidence for a strong influence of Prior Calcite Precipitation (PCP) in the aquifer above and inside the cave on the stable isotope and trace element signals. In addition, all proxy records are interpreted as evidence for past changes in precipitation and vegetation density and document a clear trend from more humid climate during early MIS 3 (ca. 57 – 50 ka) to less humid conditions during mid and late MIS 3 (ca. 45 – 30 ka).
Our multi-proxy approach thus allows us not only to precisely determine the timing, duration, and progression of several D/O events, but also to deepen our general understanding of climate variability during MIS 3 in Central Europe.
Klose, J.; Weber, M.; Vonhof, H.; Plessen, B.; Breitenbach, S.; Marwan, N.; Scholz, D.
Timing of Dansgaard-Oeschger events in Central Europe based on three precisely dated speleothems from Bleßberg Cave, Germany Konferenzberichte
Poster, 2022, (KR9 Konferenz in Innsbruck).
@proceedings{klose2022,
title = {Timing of Dansgaard-Oeschger events in Central Europe based on three precisely dated speleothems from Bleßberg Cave, Germany},
author = {J. Klose and M. Weber and H. Vonhof and B. Plessen and S. Breitenbach and N. Marwan and D. Scholz},
editor = {KR9 in Innsbruck, 2022},
url = {https://bbh.pik-potsdam.de/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/klose_KR9-Innsbruck2022.pdf},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-07-19},
urldate = {2022-07-19},
abstract = {The last glacial period and especially Marine Isotope stage 3 (MIS 3, ca. 57 - 27 ka) was characterized by various climate oscillations (i.e., rapid increases in temperature, followed by a gradual cooling, the Dansgaard-Oeschger (D/O) events), which were first discovered in Greenland ice cores. Although their causes are still not fully understood, clear evidence for their supra-regional character was found in various climate records around the globe. However, European speleothem samples, which grew during MIS 3, are limited and mainly restricted to alpine regions, where glacier meltwater enabled speleothem growth, and to south/south-western parts of Europe characterised by a generally warmer climate. This led to the opinion that it was too cold and/or too dry in central Europe for speleothem growth. Here we present three speleothem (flowstone) records from Bleßberg Cave, Germany, which grew during MIS 3.
All flowstones show episodical growth patterns with distinctive, thin growth phases. Potential contamination deriving form detrital material deposited during hiatuses between individual growth phases, open-system behaviour around the hiatuses and the limited thickness of the growth layers are the biggest challenges during sampling for 230Th/U dating. By combination of different sampling techniques (i.e., laser ablation and micro-milling) in addition to the common approach of handheld drilling and due to the relatively high 238U concentration of the samples (approx. 0.4 – 1 µg/g), we were able to date even the thinnest growth layers (< 2 mm) of the Bleßberg flowstones with a very high precision (i.e., with 2σ-age uncertainties of a few hundred years or even lower).
The timing of the growth phases of the Bleßberg flowstones correlates with several D/O events recorded in the Greenland ice cores. This proves that at least some phases of MIS 3 had favourable climate conditions for speleothem growth in Central Europe. In addition, the analysis of the stable oxygen and carbon isotopes (δ18O and δ13C) for all three flowstones revealed several D/O events, which have not been recorded in any other speleothem from central Europe so far. This will enhance our understanding of climate variability during MIS 3 and specific D/O events in central Europe.},
howpublished = {Poster},
note = {KR9 Konferenz in Innsbruck},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {proceedings}
}
All flowstones show episodical growth patterns with distinctive, thin growth phases. Potential contamination deriving form detrital material deposited during hiatuses between individual growth phases, open-system behaviour around the hiatuses and the limited thickness of the growth layers are the biggest challenges during sampling for 230Th/U dating. By combination of different sampling techniques (i.e., laser ablation and micro-milling) in addition to the common approach of handheld drilling and due to the relatively high 238U concentration of the samples (approx. 0.4 – 1 µg/g), we were able to date even the thinnest growth layers (< 2 mm) of the Bleßberg flowstones with a very high precision (i.e., with 2σ-age uncertainties of a few hundred years or even lower).
The timing of the growth phases of the Bleßberg flowstones correlates with several D/O events recorded in the Greenland ice cores. This proves that at least some phases of MIS 3 had favourable climate conditions for speleothem growth in Central Europe. In addition, the analysis of the stable oxygen and carbon isotopes (δ18O and δ13C) for all three flowstones revealed several D/O events, which have not been recorded in any other speleothem from central Europe so far. This will enhance our understanding of climate variability during MIS 3 and specific D/O events in central Europe.
Bojack, Stephan
Rekonstruktion des MIS 3 anhand von Wachstumsphasen eines präzise datierten Speläothems aus der Bleßberghöhle Bachelorarbeiten
Johannes-Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, 2022.
@bachelorthesis{bojack2022,
title = {Rekonstruktion des MIS 3 anhand von Wachstumsphasen eines präzise datierten Speläothems aus der Bleßberghöhle},
author = {Stephan Bojack},
url = {https://bbh.pik-potsdam.de/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/BSc-Arbeit-S-Bojack.pdf},
year = {2022},
date = {2022-01-01},
urldate = {2022-01-01},
school = {Johannes-Gutenberg-Universität Mainz},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {bachelorthesis}
}
