Isothermal thermoluminescence dating of speleothem growth – A case study from Bleßberg cave 2, Journal Article
In: Quaternary Geochronology, vol. 85, pp. 101628, 2024.
Isothermal thermoluminescence (ITL) dating of a speleothem from Bleßberg Cave Presentation
29.06.2023, (17th International Luminescence and Electron Spin Resonance Dating conference (LED2023), Copenhagen (Denmark)).
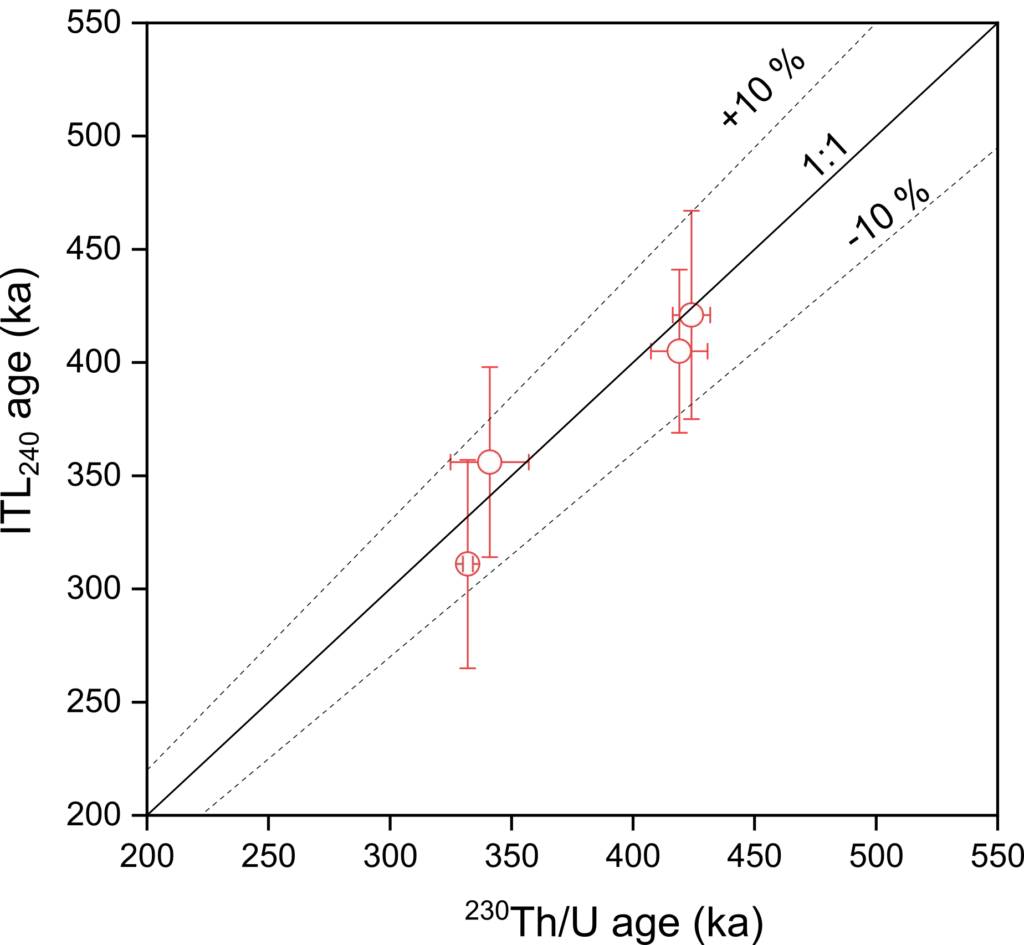
This study examines the method of isothermal thermoluminescence dating to determine the age of speleothems. Traditional methods for dating cave formations, such as U/ThU/Th-Datierung Die U/Th-Datierung ist eine sehr präzise radiometrische Altersbestimmung auf Basis der Uran-Thorium-Zerfallsreihe. Das Uran zerfällt mit bekannten Halbwertszeiten (245.500 Jahre) zum Tochterelement Thorium. Stalagmiten bauen bei ihrem Wachstum (fast) nur das wasserlösliche Uran ein, während das schlecht bewegliche Thorium zum größten Teil im Boden und Epikarst über der Höhle verbleibt. Das kann man nutzen, um die Zeit zu berechnen, die seit der Ausfällung der untersuchten Karbonatprobe vergangen ist. Moderne massenspektrometrische Verfahren erlauben Altersbestimmungen mit der U/Th-Methode bis zu 700.000 Jahren vor Heute. dating, are challenging for very old samples. At LIAG, the stalagmite BB2-1 was used to investigate how thermoluminescence dating can be adjusted to provide accurate ages. Since light exposure on the stalagmite can affect the dating results, part of the material was removed using a special acid to minimize this effect. Additionally, it was tested how light might still influence the results. The age estimates were compared with U/Th ages measured at the University of Mainz, and they are in good agreement within the margin of error. This study thus demonstrates that thermoluminescence dating can provide reliable age estimates for particularly old speleothems.